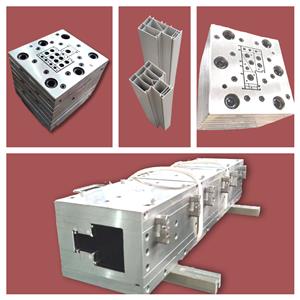
Introduction to the principle and classification of plastic extrusion molds
First, the basic principle of plastic extrusion mold The word extrude is composed of the Latin words "ex" (leave) and "trudere" (push), and the brand vividly describes the whole process of extrusion "pressing raw materials according to molds". During the production process, Zhongjie extrusion molds usually add powder or granular polymer to the extruder barrel. Under the action of a screw or plunger pump, the polymer moves forward along the screw groove or cylinder and slowly melts into mucus. Then, according to the mold set on the top of the cylinder, a continuum similar to the injection mold is generated. After refrigeration molding, it can become a necessary product, such as various plastic hose rods, plastic plates, plastic steel windows, plastic films, decorative design baseboards, etc. Develop the total key points of plastic extrusion molds. Flame retardant plastic molds are a key component of extrusion manufacturing. The technical condition of flame-retardant plastic molds immediately affects the reliability of extrusion manufacturing, the quality of extruded products, extrusion productivity and the service life of the mold itself. Therefore, the design of flame-retardant plastic molds seems to be particularly critical. In the engine design scheme, the following key points should be noted: 1. The inner wall of the engine should be streamlined. In order to make the raw materials evenly squeezed along the engine flow channel and prevent excessive decomposition reaction of raw materials due to stagnation, it is never allowed to reduce the engine amplitude, not to mention the blind zone and stagnation zone, the runner should be smooth as much as possible, and the recommended appearance roughness Ra value is 0.4μm. 2. Adequate engine compression ratio. Depending on the plastic product and type of plastic, the design scheme can produce enough engine compression ratio engine to remove the fusion seams caused by the separation bracket and make the product dense. 3. Proper cross-sectional appearance. Due to the characteristics of the plastic, working pressure, relative density, shrinkage and other factors, the cross-sectional appearance formed by the opening of the engine mold is different from the true cross-sectional appearance of the product. This factor should be considered when designing the scheme to give the engine mold opening an effective cross-sectional appearance. 4. The rhythm is tight, which is conducive to disassembly. Under the premise of achieving physical performance, the engine should be formulated with a sense of rhythm, tight connection, symmetrical thermal conduction, easy disassembly, and no leakage. 5. The assembly is effective. The engine should use stainless steel plate with corrosion resistance, wear resistance, good compressive strength and high strength. Some should also use stainless steel depending on the situation. Second, the introduction of mold classification Molds can be divided into metal molds and non-metal molds. Metal molds are further divided into: casting molds (non-ferrous metal die casting, steel casting), and forging molds; Non-metallic molds are also divided into: plastic molds and inorganic non-metallic molds. According to the different materials of the mold itself, the mold can be divided into: sand mold, metal mold, vacuum mold, paraffin mold and so on. Among them, with the rapid development of polymer plastics, plastic molds are closely related to people's lives. Plastic molds can generally be divided into: injection molding molds, extrusion molding molds, gas-assisted molding molds and so on. Mass production of non-sheet metal steel parts - cold heading , die forging, metal molds, etc. Mold sheet metal discharge--hot rolling, cold rolling, hot coil, cold coil sheet metal processing--deep drawing, shaping, bending, punching, blanking non-ferrous metals - die casting, powder metallurgy plastic parts - injection molding, blow molding (plastic bottle), extrusion (pipe fittings) mold Other classification: alloy mold, sheet metal mold, plastic mold, stamping mold, casting mold, forging mold, extrusion mold, die casting mold, automobile mold, thread rolling mold, etc.