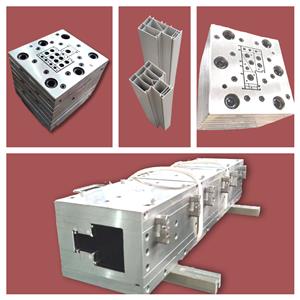
PVC plastic, the construction of the extrusion mold, unveils the veil for you
There are two forms of molds commonly used: plate stepped molds and cross-sectional gradient molds. The flow path of the plate stepped mold changes in steps, which is made of several mouth templates connected in series. Each plate is machined into a corresponding contour shape, which gradually changes from the round shape of the inlet to the desired outlet shape. There are bevels at the inlet of each block to complete the transition from one shape to another. This kind of mold processing cost is low, the flow channel is not ideal streamlined, and generally does not need to be used as the main profile. The section gradient mold runner is streamlined, there can be no retention zone of the material in the runner, the melt is gradually and accurately distributed to each section of the outlet shape from the circle at the inlet, and the speed is steadily increased to the required outlet speed, and the speed of each point on the section is the same. For PVC plastic profiles with complex mold cores, the mold core is either integrated with the bracket plate, some are fixed to the bracket plate by locating pins and screws, and some are embedded on the bracket plate by tight inlay. It cannot be easily disassembled during use, because it is time-consuming to reassemble and debug. The shunt of the melt is also carried out in two ways: on the shunt cone, and in the compression section. The section gradient mold can be used as the main profile mold. PVC plastic profile extrusion mold is the core part of the extrusion production line, which includes mouth die (also known as die head), shaping mold, cooling water tank, etc. The mouth die is assembled with the flange on the extruder head by means of a flange, and the heating ring, heating plate, power supply and thermocouple are connected. The shaping mold and cooling water tank are fixed to the shaping table with screws, and the water pipe and gas pipe are connected. The basic structure of the extrusion die is generally designed as a structure of multiple template stacked and assembled. Therefore, the flow channel of the entire die is formed by connecting one of the flow channels in each piece of the template, front and back. The platework is positioned and fastened with pins and bolts to form a monolithic extrusion die. The basic situation is: the steady flow section of the extrusion die is often composed of a perforated plate and the front half of the neck, and the front half and the second half of the neck are also designed as two templates, the neck and the neck transition plate. It is also possible not to use a porous plate, but to design the front half of the neck flow channel into a cylindrical flow channel to stabilize the flow. The split section of the extrusion die starts from the second half of the neck and includes the split cone, the split bracket plate, and the shrink plate. The shrink plate can be divided not into a single formwork, but together with the preformed plate - a formwork. The forming section of the extrusion die involves the following templates: cavity plate (also known as preformed plate), mouth template (also known as forming plate) and core (also known as mold core). For simpler profile dies, the preformed plate is combined with the mouth template into one formwork. 1. Key points of product cross-sectional design The key point of PVC plastic profile product design is that the thickness and shape of each section should be symmetrically distributed, so that the material flow in the machine head is balanced, the cooling can be uniform, and the pressure tends to be balanced. Generally speaking, the maximum wall thickness and the minimum wall thickness of the same section are different < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1